How AZTEST® Enclosures Meet GMW 3417 and GM 9538P
Back to the AZTEST Enclosure Home Page
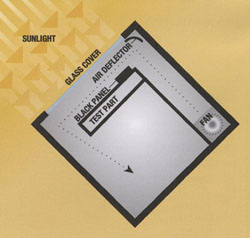 The test enclosure is a glass-covered, sealed, insulated box with controlled,
recirculating fans.
The test enclosure is a glass-covered, sealed, insulated box with controlled,
recirculating fans.
A black painted sensor located at the top edge of the specimen area continuously monitors the black-panel temperature. As sunlight enters the glass-covered enclosure, the specimen and black-panel temperatures increase. When the black-panel temperature meets or exceeds a preset temperature, a recirculating fan switches on, cooling the test specimens mounted in the enclosure.
Recirculating fans are programmed to switch on at a specific black-panel
temperatures to limit the black-panel temperature within the enclosure.
These temperatures are typically
The following two types of specimens are tested using these enclosures:
 Small flat automotive interior trim specimens.
Small flat automotive interior trim specimens.
 Full-size automotive interior parts. These test enclosures are ideal for
determining the durability of a wide variety of materials and components
used inside vehicles, including instrument panels, door panels, fabrics,
leather, seat cushions, package trays, seat belts and steering wheels.
Full-size automotive interior parts. These test enclosures are ideal for
determining the durability of a wide variety of materials and components
used inside vehicles, including instrument panels, door panels, fabrics,
leather, seat cushions, package trays, seat belts and steering wheels.
In either case, specimens are mounted 50 to 100 mm (2 to 4 inches) from the glass cover. For testing in accordance with GMW 3417 and GM 9538P, glass is typically either clear tempered or clear laminated depending on the location of the component being tested within the vehicle. For Ford DVM-0020, the glass used is PPG Solex. For ASTM G201, the glass is at the discretion of the customer.
The most common type of automotive test requires that the enclosures are set at a fixed tilt angle (typically 51 degrees from the horizontal) and tracked following the sun in azimuth (rotation). This technique provides more solar radiation and faster tests compared to fixed angle exposures. All AZTEST standard enclosures are placed on azimuth-tracking follow the sun tracking mounts.
These test enclosures offer an economical alternative to xenon-arc artificial weathering testing for small plaques. The azimuth tracking reduces test times without compromising test accuracy.
Unique to this test is a methodology to normalize solar radiant exposure based on temperature. Black-panel temperature is measured in each test enclosure every 5 minutes. On an hourly basis, TNR is calculated using the following equation:

where:
TNR = Temperature Normalized Radiation (expressed in MJ/m2 or TNR Langleys)
R = Solar Radiant Exposure (MJ/m2 or Langleys) accumulated hourly from irradiance
values measured at the test angle behind glass.
T = Temperature (°C) measured on the enclosure reference black panel.
In effect, each test enclosure has its own TNR. It is applied to the test specimens contained within that enclosure.
Each group of AZTEST Enclosures in the exposure field contains a dedicated on-board computer that controls all phases of operation. If a power outage occurs, an AZTEST Enclosures can safely shut itself down until power returns. Enclosures are totally automatic. Each enclosure contains solar cells and turns on motors to keep specimens in focus during the day.
See Typical Test Times for AZTEST Enclosures
Return to the AZTEST Enclosure Home Page
